
Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen
Lehrstuhl für Mustererkennung
Martensstraße 3
91058 Erlangen

Early detection of cancer and angiography applications are just two examples that can directly benefit from an imaging modality with excellent soft-tissue contrast. X-ray grating interferometry is promising to achieve this while keeping radiation dose and examination costs low. Existing clinical X-ray systems can be retrofitted with a set of three gratings to form an interferometer. The measurement procedure yields three images: X-ray absorption, differential phase, and dark-field. The vision of phase-contrast X-ray is that these three complementary signals together enable highly sensitive tissue contrast for medical diagnosis and interventional applications.
The X-ray phase contrast group at the Pattern Recognition Lab develops algorithms for processing these images, and for the 3-D reconstruction of tomographic acquisitions. We closely collaborate with the physicist at ECAP, who are maintaining the experimental setup.
| Date | Topic | Absence | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30.01.2019 | Journal Club: Direct access to the moments of scattering distributions in x-ray imaging | Shiyang | ||||||
| 05.02.2019 | Journal Club: Singel-image phase retrieval for hard X-ray grating interferometry | |||||||
| 11.02.2019 | - | Christian | ||||||
| 20.02.2019 | Organization | |||||||
| 28.02.2019 | Discussion on Twin images | |||||||
Literatur: [1] Short overview: Yashiro, W., et al. "X‐ray Phase Imaging and Tomography Using a Fresnel Zone Plate and a Transmission Grating." AIP Conference Proceedings. [2] Adding phase difference images: Yashiro, W., et al. "Hard-X-ray phase-difference microscopy using a Fresnel zone plate and a transmission grating." Physical review letters [3] Adaptive deconvolution algorithm based on a Bayesian framework, where the statistical distribution of error is taken into account: Yashiro, Wataru, et al. "Hard-x-ray phase-imaging microscopy using the self-imaging phenomenon of a transmission grating." Physical Review A [4] More details regarding [3] in: Lian, S., et al. "An improved phase shift reconstruction algorithm of fringe scanning technique for X-ray microscopy." Review of Scientific Instruments | ||||||||
| 06.03.2019 | Rebuttal exercise | |||||||
| 11.03.2019 | Discussion on iterative pbPCI-Reko | |||||||
Literatur: [1] Clark: Use of a complex constraint in coherent diffractive imaging [2] Hagemann: Divide and update: towards single-shot object and probe retrieval for near-field holography | ||||||||
| 20.03.2019 | tbd | Lina | ||||||
| 27.03.2019 | --- PRS --- | |||||||
| 02.04.2019 | Johannes: double sensitivity - talk and discussion | |||||||
| 10.04.2019 | Journal Club: Lee at al. - Eliminating artifacts in single-grid phase-contrast x-ray imaging for improving image quality | |||||||
| 17.04.2019 | - | |||||||
| 24.04.3029 | Journal Club: Dong et al. - A Deep Learning Reconstruction Framework for Differential Phase-Contrast Computed Tomography with Incomplete Data (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.00531.pdf) | |||||||
| 01.05.2019 | - | |||||||
| 08.05.2019 | Journal Club: 3D grating-based X-ray phase-contrast computed tomography for high-resolution quantitative assesment of cartilage: An experimental feasibility study with 3T MRI, 7T MRI and biomechanical correlation (Plos One) | |||||||
| 15.05.2019 | Journal Club: Ring artifact suppression in X-ray computed tomography using a simple, pixel-wise response correction (https://www.osapublishing.org/DirectPDFAccess/DEEE1D57-B488-02BB-66003DE0A32F7EB6_412048/oe-27-10-14231.pdf?da=1&id=412048&seq=0&mobile=no) | |||||||
| 05.06.2019 | Student Yaxin: Phase reconstruction in Ptychography | |||||||
| 12.06.2019 | - | |||||||
| 19.06.2019 | tbd | Lina | ||||||
| 26.06.2019 | preliminary! Journal Club: Clarification on Generalized Lau condition for X-ray interferometers based on dual phase gratings | |||||||
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ||||||||
| Suggestions: | Robust X-ray Sparse-view Phase Tomography via Hierarchical Synthesis Convolutional Neural Networks (https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1901/1901.10644.pdf) | |||||||
Full-field structured-illumination super-resolution X-ray transmission microscopy |
Besides our colloquium, we regularly attend the colloquium of our collaborators at ECAP, every Wednesday, 10:00, at Erwin-Rommel-Str. 1
Mailing list subscription management page for ![]() students and
students and ![]() guests.
guests.

Early detection of cancer and angiography applications are just two examples that can directly benefit from an imaging modality with excellent soft-tissue contrast. X-ray grating interferometry is promising to achieve this while keeping radiation dose and examination costs low. Existing clinical X-ray systems can be retrofitted with a set of three gratings to form an interferometer. The measurement procedure yields three images: X-ray absorption, differential phase, and dark-field. The vision of phase-contrast X-ray is that these three complementary signals together enable highly sensitive tissue contrast for medical diagnosis and interventional applications.
The X-ray phase contrast group at the Pattern Recognition Lab develops algorithms for processing these images, and for the 3-D reconstruction of tomographic acquisitions. We closely collaborate with the physicist at ECAP, who are maintaining the experimental setup.
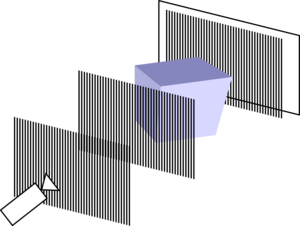
The attenuation, phase-shift and dark-field signals obtained with a Talbot-Lau system are correlated to a certain degree. The idea of this project is to leverage these correlations to improve 3-D reconstruction of image data, for example for beam hardening correction or reconstruction with a limited field-of-view.
More details can be found on Lina's ![]() project page
project page
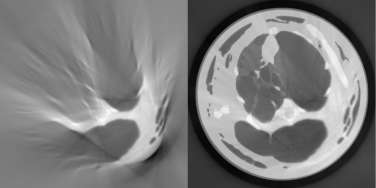
Grating-based Talbot-Lau X-ray Interferometry is a novel imaging modality. Compared to standard absorption X-ray imaging, it enables the acquisition of differential phase contrast images. These images correspond to the electron density of the scanned specimen. Furthermore, so-called dark-field images are obtained. These images can visualize density inhomogeneities at micrometer scale. The goal of the project is to improve the setup of Talbot-Lau X-ray Imaging systems. So far the correlation between the different variables of such a system especially with polychromatic X-ray spectra is not known yet. Thus, the setup should be simulated and optimized to find the ideal setup with respect to certain structures in the object and the resulting images.
More details can be found on Johannes' ![]() project page
project page

X-ray dark-field imaging (XDI) measures ultra-small angle scattering. It allows reconstruction of structural variation at length scales from hundreds nanometers to some micrometers, which is much smaller than the resolution of a conventional X-ray imaging system. The core idea of this project is to develop algorithms to fully recover information from XDI datasets.
More details can be found on Shiyang's ![]() project page
project page
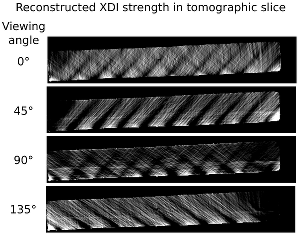


X-ray dark-field imaging (XDI) measures ultra-small angle scattering. It allows reconstruction of structural variation at length scales from hundreds nanometers to some micrometers, which is much smaller than the resolution of a conventional X-ray imaging system. The core idea of this project is to develop algorithms to fully recover information from XDI datasets.
More details can be found on Shiyang's ![]() project page
project page
Grating-based Talbot-Lau X-ray Interferometry is a novel imaging modality. Compared to standard absorption X-ray imaging, it enables the acquisition of differential phase contrast images. These images correspond to the electron density of the scanned specimen. Furthermore, so-called dark-field images are obtained. These images can visualize density inhomogeneities at micrometer scale. The goal of the project is to improve the setup of Talbot-Lau X-ray Imaging systems. So far the correlation between the different variables of such a system especially with polychromatic X-ray spectra is not known yet. Thus, the setup should be simulated and optimized to find the ideal setup with respect to certain structures in the object and the resulting images.
More details can be found on Johannes' ![]() project page
project page
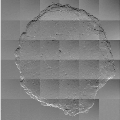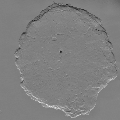
The imaging performance of grating-based interferometers can be impacted by imperfections of the gratings and system miscalibration. The first goal of this project is to develop novel algorithms for correcting measurement artifacts in phase contrast images. The second goal is to investigate the problem of retrieving the X-ray phase shift from the differential projections by integration and its impact on object detectability.
More details can be found on Sebastian's ![]() project page.
project page.
The imaging performance of grating-based interferometers can be impacted by imperfections of the gratings and system miscalibration. The first goal of this project is to develop novel algorithms for correcting measurement artifacts in phase contrast images. The second goal is to investigate the problem of retrieving the X-ray phase shift from the differential projections by integration and its impact on object detectability.
More details can be found on Sebastian's ![]() project page.
project page.

The goal of this project is to build and investigate a system and algorithms for 2-D tomographic phase reconstruction using an X-ray grating interferometer. The system is built at ![]() ECAP. The system software was developed in large part by
ECAP. The system software was developed in large part by ![]() Wilhelm Haas, former member of the Pattern Recognition Lab.
Wilhelm Haas, former member of the Pattern Recognition Lab.


The goal of this project is to build and investigate a system and algorithms for 2-D tomographic phase reconstruction using an X-ray grating interferometer. The system is built at ![]() ECAP. The system software was developed in large part by
ECAP. The system software was developed in large part by ![]() Wilhelm Haas, former member of the Pattern Recognition Lab.
Wilhelm Haas, former member of the Pattern Recognition Lab.